| Spectral Color |
A wav length of electromagnetic radiation that falls within the visible spectrum. |
The term spectral color contrasts with the term perceptual color, or simply color. |
| Color |
A perception of color that can arise from sensory stimulation by a single spectral color or by a mixture of primary spectral colors. |
The unmodified term color refers to perceptual color as represented on the color wheel. Since the spectral colors fall in a linear range, but perceptual colors that are produced by mixing primary colors form a color wheel, some perceptual colors do not correspond to any single spectral color. |
| Primary Color |
One of a small number of colors that can be mixed together to produce the same impression as any of a wide range (gamut) of colors. |
|
| Color Model |
One of the general methods used in digital graphics to represent colors in terms of numbers that may correspond to a small number of primary colors or a small number of dimensions. |
Note that the human eye works by comparing the output of 3 types of receptors that have their peak output very approximately at three primary colors. Illustrator supports three color models RGB, CMYK, and HSB. |
| Color Space |
A subset of all the colors, which may depend on the medium, the output device, and the manufacture. |
Examples Adobe RGB, Apple RGB, and sRGB. |
| Color Gamut |
A range of colors in a Color Space. |
|
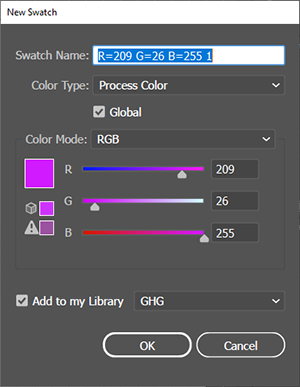
| RGB |
A color model that represents all colors by mixing together the three primary colors: Red, Green, and Blue light. |
This model is called an additive model, because each color is produced by adding together red, green, and blue lights. Any combination of these three lights that stimulates all three human color receptors equally will produce gray. Used in light generating devices such as TVs and monitors. |
| CMYK |
A color model that represents all colors by mixing together the three primary colors: Cyan (C), magenta (M), and yellow (Y), plus black (K). The "K" stands for the key color. These four colors are called process colors. |
This model is called a subtractive model, because each color is produced by mixing together cyan, magenta, and yellow, and black pigments, that absorbed (subtract) light that is reflected to the eye. Printing that uses some mixture of cyan, magenta, and yellow, and black ink is called four-color process printing. A color specified as a mixture of these colors is called a process color, as opposed to a spot color. Because it depends on reflected light, CMYK has a smaller color gamut than does RGB. |
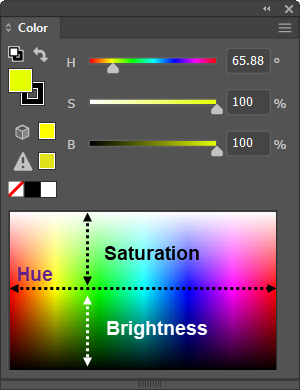
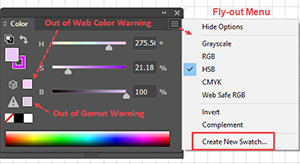
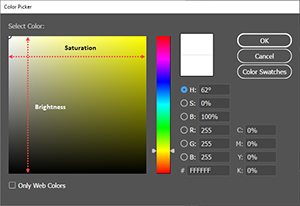
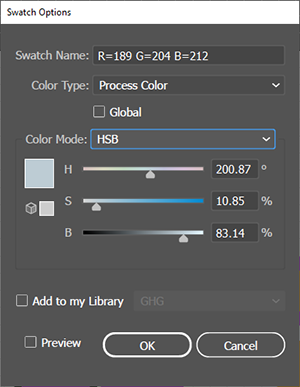
| HSB |
A color model that represents subjective colors in terms of three numerical dimensions: Hue, Saturation, and Brightness. Hue is a number between 0 and 360 that represents an angle on a standard color wheel. Saturation is a percentage value between 0% (no color, i.e., gray) and 100% (i.e., pure color, fully saturated). Brightness (i.e., the luminosity, or gray scale value) is a value between 0% and 100%; where 0% corresponds to black, and 100% corresponds to white. |
For output devices, a HSB color must be simulated by some RGB or CMYK color. |
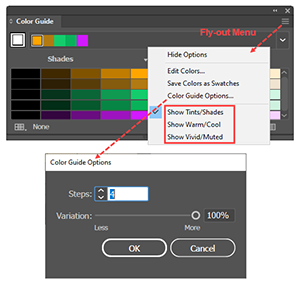
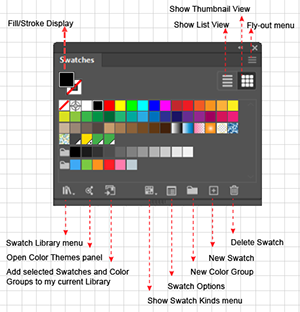
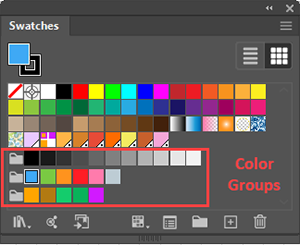
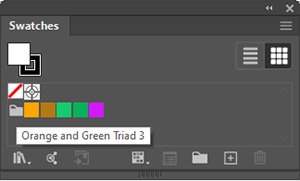
| Global Swatch |
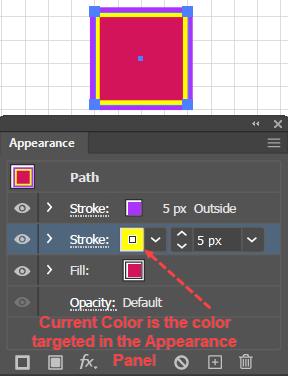
An Adobe Illustrator term that refers to a feature that allows you to designate a swatch's color mix as Global. A Global swatch remains associated with all instances where you have used the Global swatch, and when you update a Global swatch, all the places where you have used instances of the Global color swatch will automatically update. In the Swatches Panel, Illustrator flags a swatch as Global by placing a small white triangle in the lower right corner of the swatch icon. |
In illustrator, a Global Color is a software object known as a class or type. The software class allows you to treat a fill or stroke where you used that color, not as an isolated object property, but as one of a class of properties that were made using that swatch. Global colors are useful, for example for maintaining a corporate color palette. |
| Spot Color |
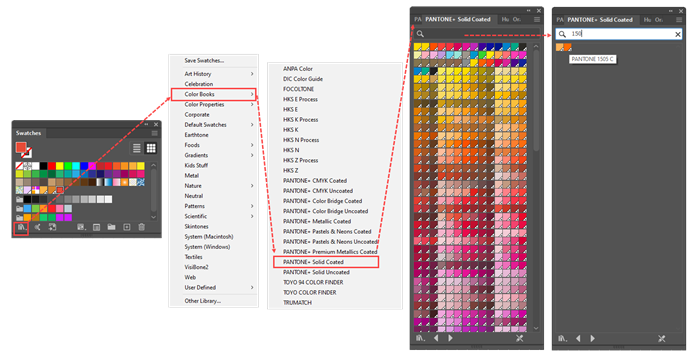
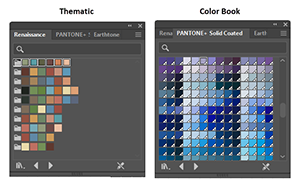
A term used in the printing industry to describe a color that is mixed on the press and often specified in an industry standard formula guide library. These libraries (e.g., PANTONE Solid Coated) specify appropriate ink formulas for particular types of paper. To find these in the Swatches panel, you click the Swatch Libraries menu icon and then on the popup menu select Color Books. Illustrator represents a spot color swatch with the same (small white triangle in the lower right corner) as it does for a Global color, but it puts a dot in the triangle. |
Contrasts with Process Color. The color that appears on your computer monitor is an RGB simulation of an industry standard color. The final printed color will depend on the printers choice of paper, ink mixing process, and varnish. Spot colors are used, for example, to print a company logo that is specified by brand marketing guidelines. |
| Process Color |
A term used in the printing industry to describe a printing process that uses the four CMYK colors. |
Used for printing jobs (such as photographs) that require many different mixtures of inks to represent many subjective colors. A process color application contrasts with, for example, a 3 (spot) color printing job, which might be all that is needed to accurately print the corporate logo, and another highlight color. |